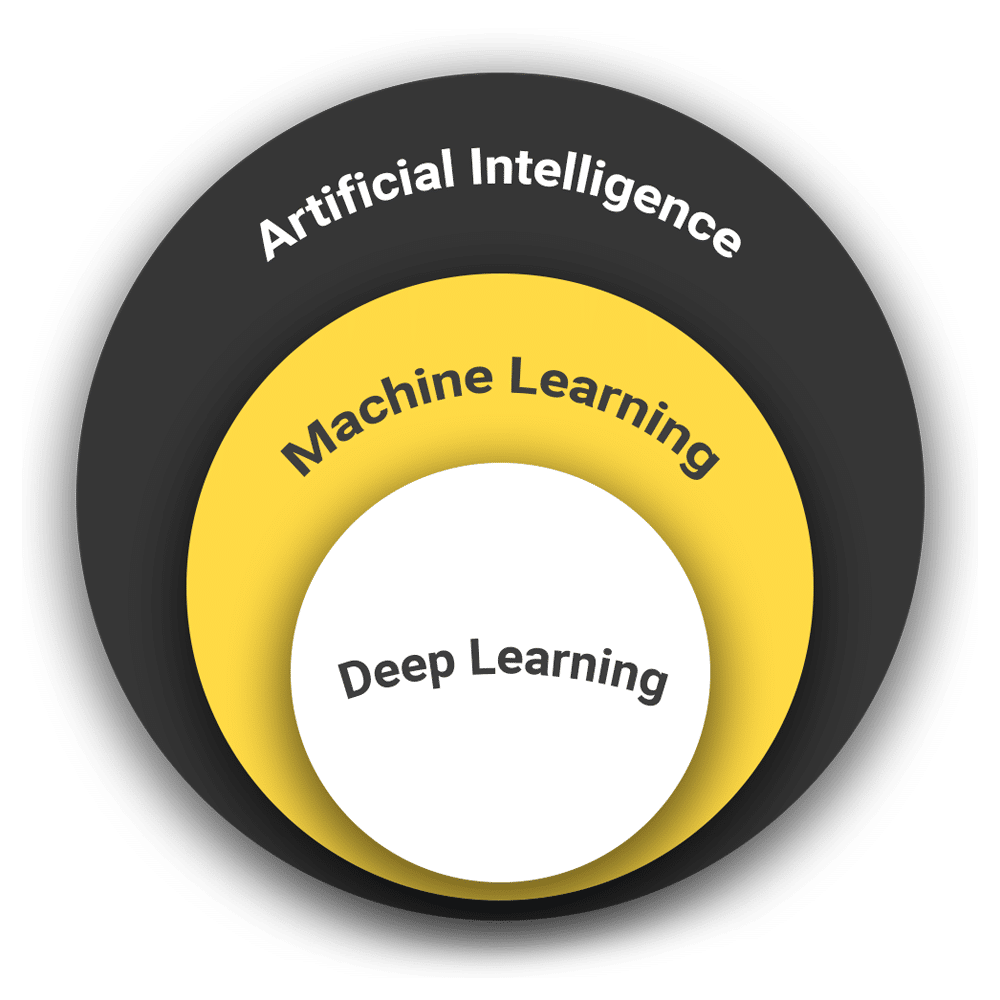
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The study of how to train computers so they can handle tasks traditionally attributed to humans. In other words, it means training computers so that someday they can take over tasks in which they are more efficient than humans.
A landmark application of AI has been in x-ray analysis, in which a computer can be extra sensitive to light patterns and recognise trends based on a volume of data that is out of the reach of most humans.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is the process through which an AI entity can learn new things from experience, without the need for being taught. This requires the exposition of AI to a large amount of data with the validation of results being conducted in parallel by both humans and AI itself.
This way an AI can recognise new information on its own and generate new information from apparently disconnected data using self learning algorithms.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning in artificial intelligence (AI) that comprises networks capable of unsupervised learning, from data that is unstructured or unlabelled.
Also known as deep neural learning or deep neural network, these algorithms and infrastructures can learn without human dependency. Also known as deep neural.